用于评估冠状动脉疾病的3D模型
在学报发表的一篇文章中医生杂志》上al Imaging (JMI), researchers announce critical advances in the use of 3D-printed coronary phantoms with diagnostic software, further developing a non-invasive diagnostic method for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) risk assessment.
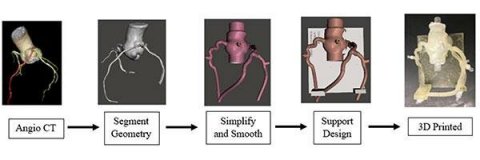
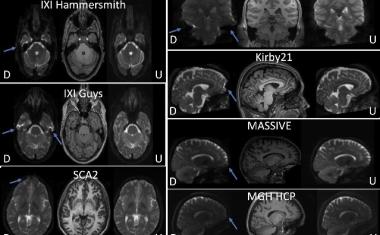
医生已经使用了计算机断层摄影 - 分数流量储备(CT-FFR)诊断软件的非侵入性方法来表征血液流动,以评估CAD的风险。CT-FFR使用心脏的CT图像与计算方法组合,以估算动脉中的血流条件。CT-FFR的一个关键缺点在于验证CT-FFR诊断软件,需要与地面真理进行大型临床试验。本篇论文讨论的幻影模型从真正的患者复制脉管系统,允许在提供弹性性质的情况下进行实际血流的生理测试,并且可用于有效地验证CT-FFR软件。
The research, delineated in the open-access article, “Initial evaluation of 3D printed patient-specific coronary phantoms for CT-FFR software validation,” demonstrates the utilization of coronary phantoms to accurately assess intermediate-risk patients’ Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR), the measurement that determines CAD severity. The research also expands on the current applications of 3D printing to further develop cardiac phantoms with structures closely mimicking patient anatomies, allowing for accurate CT imaging of coronary flow.
In this study, CT scans of these phantom cardiac models were accurate to within 1mm diameter of the actual patients’ hearts, and the research team expects that accuracy to increase as the resolution of CT scanners and 3D printers improve. “This exceptional paper highlights an important step forward in the use of 3D-printing of patient-specific coronary models and their contribution to assessing vasculature blood flow. It provides a critical requirement to validate the CT-FFR calculation using a phantom, thus enabling an efficient mechanism to ascertain the accuracy and reliability of CT-FFR estimation methods. This lends a strong support to the ongoing paradigm shift in CAD risk assessment via CT-FFR,” says Dr. Ehsan Samei, JMI Associate Editor, SPIE Fellow, and Professor of Radiology at Duke University.
来源:SPIE