Sensor fusion device for non-contact measurement of vital signs
A researcher has developed a multiple sensor fusion device for non-contact measurement of vital signs and its clinical applications.
There is increasing interest in technology for non-contact measurement of human vital signs (heart rate, respiration, and body temperature), which are important for understanding the state of a person’s health. New biological measurement sensors have been developed as well as reports on methods for measuring respiration or heartbeat using pressure sensors, microwave radar, RGB camera, and thermography. This technology has wide-ranging applications. Guanghao Sun’s group is developing clinical applications for monitoring elderly people, identification of sleep apnea, detection of patients who may carry infectious diseases, and noncontact measurement of stress levels.
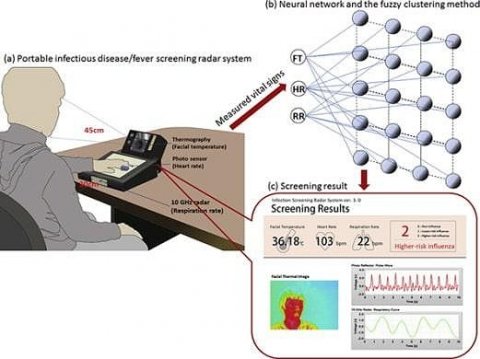
The outbreak of infectious diseases such as swine flu (H1N1) and avian flu (H5N1) are a threat to global health. To prevent and control the spread of infectious diseases, many international airport quarantine areas have adopted fever-based screening using infrared thermography to identify potentially infected individuals. Unfortunately, some studies indicate that fever-based screening at early-stages of infectious diseases is limited due to factors that can affect thermographic measurements, such as antifebrile intake, alcohol consumption, and ambient temperatures.
Guanghao Sun has proposed an infection screening system that can rapidly and accurately perform medical inspections. As a result of being infected, not only body temperature but also heart and respiration rates increase. Sun’s system automatically detects infected individuals within 15 seconds by a discriminant function using measured vital signs. Heart and respiration rates are determined using a 24-GHz microwave radar by noncontact way, and facial skin temperature is monitored by a thermographic camera. By using these three parameters, the detection accuracy of the system improved to 88% in a case control study. This is notably higher compared to the conventional screening methods using only thermography.
Remote monitoring of respiratory rate
The use of continuous and long‐term monitoring of respiratory rate is vital for predicting pneumonia in symptomatic patients. However, it is often measured manually and discontinuously by counting chest wall movements in routine practice. Sun has developed a point‐of‐care system for the early detection of pneumonia in symptomatic elderly bedridden hospitalized patients on the basis of 24‐hours continuous and noncontact monitoring of respiratory rate using a medical radar sensor.
Sun focused on designing a system that would improve hospitalized patient quality of life and reduce medical staff workload. To this end, the system adopts a medical radar sensor for respiration monitoring that featured an extremely low burden on the patient and enabled unobtrusive measurements without the need to attach electrodes to the patient’s body. To reduce medical staff workload, a prediction method, that is, return map, was implemented into the system to analyze the time series respiratory rates, thereby extracting the risk period of pneumonia and sending out an alarm. The novelty of the proposed system is that it introduces a new approach to investigating respiration dynamics using a noncontact medical radar sensor for the early prediction of pneumonia that has the potential to serve as a helpful tool for improving patient quality of life and reduce medical staff workload to meet the needs of the aging society.
Source:大学电子通信