A biosensor for the COVID-19 virus
来自Empa,Eth苏黎世和苏黎世大学医院的一支研究人员成功地开发了一种用于检测新冠状病毒的新型传感器。在未来,它可以用来测量环境中病毒的浓度 - 例如在有许多人或医院通风系统中的地方。

Empa和Eth苏黎世的景王和他的团队通常致力于测量,分析和减少气溶胶等空气污染物,也在人工制作nanoparticles。然而,全世界目前面临的挑战也在改变研究实验室的目标和策略。新的焦点:一个可以快速可靠地检测SARS-COV-2的传感器 - 新的新冠病毒。
但是这个想法并不是从集团之前的研究工作中删除了:甚至在之前COVID-19began to spread, first in China and then around the world, Wang and his colleagues were researching sensors that could detect bacteria and viruses in the air. As early as January, the idea of using this basis to further develop the传感器in such a way that it could reliably identify a specific virus was born. The sensor will not necessarily replace the established laboratory tests, but could be used as an alternative method for clinical diagnosis, and more prominently to measure the virus concentration in the air in real time: For example, in busy places like train stations or hospitals.
Fast and reliable tests for the new coronavirus are urgently needed to bring the pandemic under control as soon as possible. Most laboratories use a molecular method called reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, or RT-PCR for short, to detect viruses in呼吸道感染。这是完全建立的,可以检测到甚至少量的病毒 - 但同时它可能是耗时和容易出错的时间。
An optical sensor for RNA samples
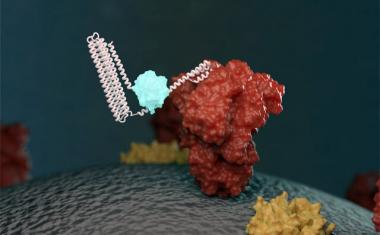
景王和他的团队以光学的形式开发了一种替代测试方法生物传感器。传感器结合了两种不同的效果来安全地且可靠地检测病毒:光学和热量。
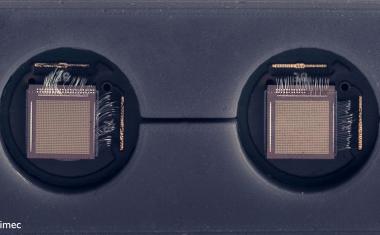
该传感器基于玻璃基板上的金色所谓的金纳米纳米纳米的微小结构。人工产生的DNA受体匹配具体RNA序列of the SARS-CoV-2 are grafted onto the nanoislands. The coronavirus is a so-called RNA virus: Its genome does not consist of a DNA double strand as in living organisms, but of a single RNA strand. The receptors on the sensor are therefore the complementary sequences to the virus' unique RNA sequences, which can reliably identify the virus.
The technology the researchers use for detection is called LSPR, short for localized surface plasmon resonance. This is an optical phenomenon that occurs in metallic nanostructures: When excited, they modulate the incident light in a specific wavelength range and create a plasmonic near-field around the nanostructure. When molecules bind to the surface, the local refractive index within the excited plasmonic near-field changes. An optical sensor located on the back of the sensor can be used to measure this change and thus determine whether the sample contains the RNA strands in question.
热increases reliability
然而,重要的是,只捕获与传感器上的DNA受体恰好匹配的那些RNA链。这是第二种效果在传感器上发挥作用的地方:等离子体光热(PPT)效应。如果传感器上的相同纳米结构与某个波长的激光激发,则产生局部热量。
And how does that help reliability? As already mentioned, the genome of the virus consists of only a single strand of RNA. If this strand finds its complementary counterpart, the two combine to form a double strand - a process called hybridization. The counterpart - when a double strand splits into single strands - is called melting or denaturation. This happens at a certain temperature, the melting temperature. However, if the ambient temperature is much lower than the melting temperature, strands that are not complementary to each other can also connect. This could lead to false test results. If the ambient temperature is only slightly lower than the melting temperature, only complementary strands can join. And this is exactly the result of the increased ambient temperature, which is caused by the PPT effect.
为了证明新的传感器如何检测到当前的Covid-19病毒,研究人员用非常密切相关的病毒测试:SARS-COV。这是2003年爆发的病毒,并引发了SARS大流行。两种病毒 - SARS-COV和SARS-COV2 - 仅在其RNA中略微不同。验证成功:“测试表明,传感器可以清楚地区分两种病毒的非常相似的RNA序列,”景王解释道。结果在几分钟内准备好了。
然而,此时,传感器尚未准备好测量空气中的电晕病毒浓度,例如在苏黎世的主要火车站。仍然需要许多发育步骤来执行此操作 - 例如,在空中绘制的系统,将气溶胶浓缩并释放来自病毒的RNA。“这仍然需要开发工作,”王说。但是,一旦传感器准备就绪,原则就可以应用于其他病毒,并帮助在早期阶段检测和停止流行病。
资源:empa.