AI.-controlled sensors could save lives in 'smart' hospitals
Researchers explain how computer scientists and clinicians are trying to reduce fatal medical errors by building “ambient intelligence” into the spaces where patients reside.
由于医疗错误,每年有多达400,000名美国人死亡,但使用电子可以防止这些死亡中的许多死亡sensorsand人工智能to help medical professionals monitor and treat vulnerable patients in ways that improve outcomes while respecting privacy. “We have the ability to build technologies into the physical spaces where health care is delivered to help cut the rate of fatal errors that occur today due to the sheer volume of patients and the complexity of their care,” said Arnold Milstein, a professor of medicine and director of Stanford’s Clinical Excellence Research Center (CERC).
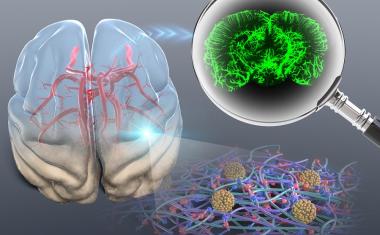
Milstein, along with computer science professor Fei-Fei Li and graduate student Albert Haque, are co-authors of aNature paperthat reviews the field of “ambient intelligence” in health care — an interdisciplinary effort to create suchsmart hospital配备AI系统的客房可以做一系列以改善结果。例如,当在进入医院房间之前,传感器和AI可以立即提醒临床医生和患者访客。AI工具可以内置于智能家居中,在那里技术可以不引人注目地监控难以消除的脆弱年龄的脆弱性危机的线索。他们迅速在家里的照顾者,远程定位临床医生和患者自己,以及时,挽救生命的干预措施。
李,他是斯坦福大学研究所的主任or Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI), said ambient technologies have many potential benefits, but they also raise legal and regulatory issues, as well as privacy concerns that must be identified and addressed in a public way to win the trust of patients and providers, as well as the various agencies and institutions that pay health care costs. “Technology to protect the health of medically fragile populations is inherently human-centered,” Li said. “Researchers must listen to all the stakeholders in order to create systems that supplement and complement the efforts of nurses, doctors and other caregivers, as well as patients themselves.”
Li and Milstein co-direct the 8-year-old Stanford Partnership in AI-Assisted Care (PAC), one of a growing number of centers, including those at Johns Hopkins University and the University of Toronto, where technologists and clinicians have teamed up to develop ambient intelligence technologies to help health care providers manage patient volumes so huge — roughly 24 million Americans required an overnight hospital stay in 2018 — that even the tiniest margin of error can cost many lives.
“我们在床边护理的复杂性中,我们在脚踏赛中,”Milstein说。“近期统计数据,医院新生儿重症监护病房的临床医生每天患有600次床头旁的床头员行动。没有技术援助,完美执行这一体积的复杂行动远远超出了甚至期望最具认真的临床团队的合理性。“
The Fix: Invisible light guided by AI?
哈克被编制在自然文章中引用的170篇科学论文,表示,该领域主要基于两种技术趋势的收敛性:红外传感器的可用性足以建立在高风险保育环境中,以及机器学习系统的兴起作为一种使用传感器输入来培训医疗保健中专门的AI应用的方法。
The infrared technologies are of two types. The first is active infrared, such as the invisible light beams used by TV remote controls. But instead of simply beaming invisible light in one direction, like a TV remote, new active infrared systems use AI to compute how long it takes the invisible rays to bounce back to the source, like a light-based form of radar that maps the 3D outlines of a person or object.
这种红外深度传感器already being used outside hospital rooms, for instance, to discern whether a person washed their hands before entering and, if not, issue an alert. In one Stanford experiment, a tablet computer hung near the door shows a solid green screen that transitions to red, or some other alert color that might be tested, should a hygiene failure occur. Researchers had considered using audible warnings until medical professionals advised otherwise. “Hospitals are already full of buzzes and beeps,” Milstein said. “Our human-centered design interviews with clinicians taught us that a visual cue would likely be more effective and less annoying.”
These alert systems are being tested to see if they can reduce the number of ICU patients who get nosocomial infections — potentially deadly illnesses contracted by patients due to failure of other people in the hospital to fully adhere to infection prevention protocols.
第二种红外技术是被动探测器,其排序允许夜视护目镜从体热产生的红外线产生热图像。在医院环境中,ICU床上上方的热传感器将使控制AI能够检测纸张下方的抽搐或扭动,并警觉临床团队成员到即将到来的健康危机,而不会经常从房间到房间。
So far, the researchers have avoided using high-definition video sensors, such as those in smartphones, as capturing video imagery could unnecessarily intrude on the privacy of clinicians and patients. “The silhouette images provided by infrared sensors may provide data that is sufficiently accurate to train AI algorithms for many clinically important applications,” Haque said.
Constant monitoring by ambient intelligence systems in a home environment could also be used to detect clues of serious illness or potential accidents, and alert caregivers to make timely interventions. For instance, when frail seniors start moving more slowly or stop eating regularly, such behaviors can presage depression, a greater likelihood of a fall or the rapid onset of a dangerous health crisis. Researchers are developing activity recognition algorithms that can sift through infrared sensing data to detect changes in habitual behaviors, and help caregivers get a more holistic view of patient well-being.
隐私特别关注家园,协助生活设施和养老院,但“我们来自医院和日常生活空间的初步结果证实,环境传感技术可以提供所需的数据,”Milstein表示,我们需要遏制医疗错误。““我们的自然评论告诉领域我们在正确的轨道上。”
Source:斯坦福大学