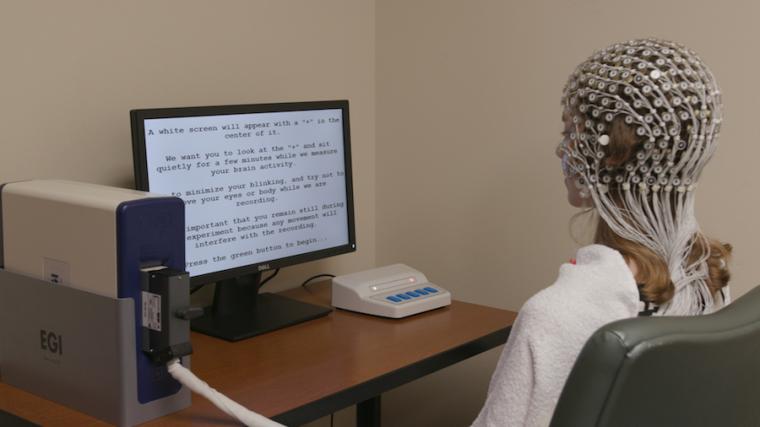
ai可能会改变医生如何治疗抑郁症
Artificial intelligence may soon play a critical role in choosing which depression therapy is best for patients. A national trial initiated by UT Southwestern in 2011 to better understand mood disorders has produced what scientists are calling the project's flagship finding: a computer that can accurately predict whether an antidepressant will work based on a patient's brain activity.
The new research is the latest among several studies from the trial that cumulatively show how high-tech strategies can help doctors objectively diagnose and prescribe沮丧治疗。虽然实施这些方法需要时间,但研究人员预测AI等工具,脑成像, 和blood tests将在未来几年彻底改变精神科学领域。“这些研究取得了比我们团队中的任何人都能想象的更大成功,”Madhukar Trivedi,M.Di,Mandhukar Trivedi,Madhukar Trivedi,Madhukar Trivei,Madhukar Trivedirs监督涉及斯坦福,哈佛及其他机构的多网站审判。“我们提供了丰富的数据来表明我们可以通过猜测抑郁症治疗的猜测游戏,并改变如何诊断疾病和治疗的疾病的心态。”
EEG-based predictions
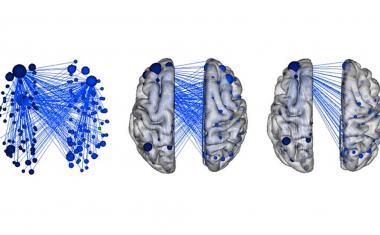
The study published in Nature Biotechnology included more than 300 participants with depression who were randomly chosen to receive either a placebo or an SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor), the most common class of antidepressant. Researchers used an electroencephalogram, or EEG, to measure electrical activity in the participants' cortex before they began treatment. The team then developed amachine learningalgorithm to analyze and use the EEG data to predict which patients would benefit from the medication within two months.
不仅AI准确预测结果,进一步的研究表明,怀疑对抗抑郁药做出疑问的患者可能会改善心理治疗或脑刺激等其他干预措施。
调查结果在三个另外的患者组中验证。“This study takes previous research, showing that we can predict who benefits from an antidepressant, and actually brings it to the point of practical utility,” says Amit Etkin, M.D., Ph.D., a Stanford University psychiatry professor who worked with Trivedi to develop the algorithm.
研究人员表示,在下一个步骤中,正在开发一种AI界面,可以广泛与全国脑电图共识,并寻求美国食品和药物管理局的批准。
Signatures of depression
Data from the study derive from the 16-week EMBARC trial, which Trivedi initiated at four U.S. sites to establish biology-based, objective strategies to remedy mood disorders.
该项目通过脑成像和各种DNA,血液和其他测试评估了主要抑郁症的患者。他的目标是解决他引导的另一个研究的令人不安的发现(明星* d),发现最多三分之二的患者不会充分应对他们的第一抗抑郁药。“我们进入了这个思考,”在治疗开始时不会更好地识别哪些患者的治疗是什么?“”Trivedi解释道。
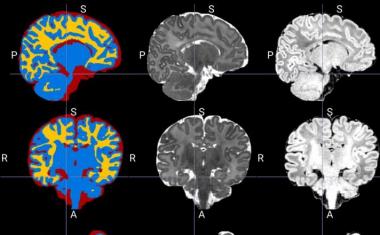
Previous EMBARC studies identified various predictive tests, including the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to examine brain activity in both a resting state and during the processing of emotions. EEG will likely be the most commonly used tool, Trivedi says, because it's less expensive and – in most cases – will be equally or more effective.
但是,血液测试或MRImay be needed for some patients if the depression is manifesting itself in a different way. "There are many signatures of depression in the body," Trivedi says. "Having all these tests available will improve the chances of choosing the right treatment the first time."
不断增长的问题
According to data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, antidepressant use in the U.S. has increased nearly 65% over a decade and a half – from 7.7% in 1999-2002 to 12.7% in 2011-2014. Trivedi says the expanded use of medications makes it more critical to further understand the underpinnings of depression and ensure patients are prescribed an effective therapy.
虽然他的团队继续评估来自Embarc试验的数据,但Trivedi已经启动了其他大型研究项目,以帮助提高抑郁症的缓解率。其中是D2K,一项研究,将注册抑郁症和双相障碍的2,500名患者,并遵循它们20年。此外,RAD是对2,500名参与者(10-24岁)的10年的研究,揭示了降低发展情绪或焦虑症的风险的因素。
Utilizing some of these enrollees, Trivedi’s research team will study the results from several other tests to assess patients’ biological signatures to determine the most effective treatment. "It can be devastating for a patient when an antidepressant doesn't work," Trivedi says. "Our research is showing that they no longer have to endure the painful process of trial and error."